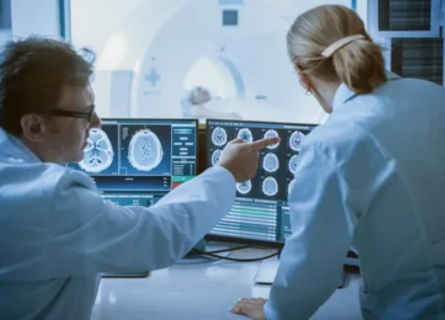
Radiologists play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of various diseases. Using advanced imaging techniques, they provide detailed insights into the body’s internal structures, helping to detect abnormalities early and guide treatment decisions. In this article, we delve into how radiologists diagnose diseases, with expert insights from DNB (Radiology) specialists like Dr. Snehal Suryawanshi, a renowned radiologist with 12 years of experience, practicing at a clinic located in Thergaon, Pune.
The Role of Radiologists in Healthcare
Radiologists are specialized medical doctors who diagnose and treat diseases and injuries through various medical imaging techniques. These techniques include:
- X-rays: Used primarily for imaging bones, detecting fractures, and monitoring the progress of diseases like arthritis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: Provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body, useful for diagnosing conditions affecting soft tissues, such as tumors and internal bleeding.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Utilizes powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of organs and tissues, particularly useful for brain, spinal cord, and joint imaging.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of organs and structures inside the body, commonly used in obstetrics, cardiology, and detecting abdominal conditions.
- Nuclear Medicine: Involves the use of small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases, especially useful for detecting cancers, heart disease, and certain neurological disorders.
Diagnostic Process in Radiology
Patient History and Clinical Information
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and clinical information. This step is critical as it guides the radiologist in choosing the most appropriate imaging modality and protocol. Information such as the patient’s symptoms, previous medical conditions, and any prior imaging studies is essential.
Imaging Examination
Once the appropriate imaging technique is selected, the patient undergoes the imaging examination. Each modality has specific protocols to ensure the highest quality images are obtained. For example:
- X-rays: Patients are positioned in a way that allows the targeted body part to be imaged clearly. Sometimes, multiple views are taken to get a comprehensive picture.
- CT Scans: Patients lie on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. They may receive a contrast agent to enhance the images.
- MRI: Patients lie inside a large tube-like machine. The procedure can take longer than other imaging techniques, and patients must remain still to obtain clear images.
- Ultrasound: A handheld device called a transducer is moved over the area of interest, often with the application of a gel to improve contact.
- Nuclear Medicine: Patients receive a small amount of radioactive material, either orally or via injection, and then lie under a special camera that detects the radiation emitted from the body.
Image Interpretation
After the images are obtained, the radiologist meticulously examines them to identify any abnormalities. This involves:
- Analyzing Structures: Radiologists assess the size, shape, and position of organs and tissues.
- Identifying Abnormalities: They look for signs of disease such as tumors, fractures, infections, or blockages.
- Comparing with Previous Images: Comparing current images with past ones helps to monitor the progression or resolution of a disease.
- Utilizing Expertise: Radiologists use their extensive training and experience to differentiate between normal variations and pathological changes.
Reporting Findings
Once the images are interpreted, the radiologist compiles a detailed report outlining their findings. This report includes:
- Description of Findings: A detailed account of any abnormalities observed.
- Clinical Correlation: Suggestions for further diagnostic tests or follow-up imaging if necessary.
- Recommendations: Possible treatment options or referrals to specialists.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
Radiologists work closely with other healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians, surgeons, and specialists, to ensure a comprehensive approach to patient care. Their insights are crucial in developing effective treatment plans and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions.
Advanced Techniques and Innovations
Radiology is a constantly evolving field with numerous advancements enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Some of the latest innovations include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms assist in analyzing imaging data, improving the detection of subtle abnormalities and streamlining workflows.
- 3D Imaging and Printing: Advanced imaging techniques allow for the creation of 3D models of organs and structures, aiding in pre-surgical planning and patient education.
- Molecular Imaging: Provides detailed information at the molecular and cellular levels, helping to detect diseases at an earlier stage.
Summary
Radiologists are integral to modern healthcare, providing critical insights into the diagnosis and management of diseases. Their expertise, combined with advanced imaging technologies, enables early detection and precise treatment planning. For patients in Pune seeking expert radiological care, Dr. Snehal Suryawanshi, DNB (Radiology), FMF, with her clinic located in Thergaon, Pune, stands out as one of the best radiologists in the region, boasting 12 years of experience in the field.