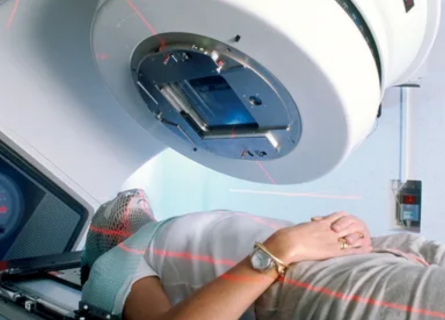
Radiation therapy stands as a cornerstone in the battle against cancer, employing high-energy radiation to target and eliminate cancerous cells. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore radiation therapy in depth, including its various treatment modalities, potential side effects, and essential coping strategies. Our insights are bolstered by the expertise of Dr. Snehal Suryawanshi, a distinguished radiologist with 12 years of experience and esteemed as the best in Pune, practicing at a reputable clinic in Thergaon.
What is Radiation Therapy?
Radiation therapy, also referred to as radiotherapy, encompasses a range of techniques aimed at eradicating cancer cells by delivering focused doses of radiation. It is a pivotal component of cancer treatment, often used alongside surgery and chemotherapy to achieve optimal outcomes.
Types of Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT):
EBRT involves directing radiation beams from an external machine onto the tumor site. This precise targeting minimizes radiation exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. Advanced technologies such as Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) enhance treatment accuracy and effectiveness.
Brachytherapy:
Brachytherapy entails the placement of radioactive sources directly into or near the tumor. This approach delivers a concentrated dose of radiation while sparing healthy tissues, making it particularly beneficial for gynecological, prostate, and skin cancers.
Treatment Planning and Delivery
Before commencing radiation therapy, a meticulous treatment plan is crafted by a multidisciplinary team comprising oncologists, radiation therapists, and medical physicists. Key considerations in treatment planning include:
Target Volume Definition: Precisely delineating the target area for radiation delivery based on imaging studies and clinical assessments.
Dose Optimization: Determining the optimal radiation dose to maximize tumor control while minimizing adverse effects on healthy tissues.
Fractionation Schedule: Establishing the frequency and duration of radiation sessions (fractions) tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
During treatment sessions, patients are positioned on a treatment table, and specialized equipment delivers radiation according to the prescribed treatment plan. Treatment sessions are typically brief, lasting only a few minutes, and patients can resume their daily activities afterward.
Potential Side Effects
While radiation therapy is highly effective in targeting cancer cells, it can also induce side effects, which may vary in severity and duration. Common side effects include:
Skin Reactions: Redness, irritation, dryness, and changes in skin pigmentation are common in the treated area. Proper skin care and moisturization can alleviate these symptoms.
Fatigue: Feeling tired or experiencing low energy levels, especially towards the latter stages of treatment, is common but temporary.
Nausea and Digestive Disturbances: Radiation to abdominal or pelvic regions may cause nausea, diarrhea, or changes in bowel habits. Dietary adjustments and medications can manage these symptoms.
Hair Loss: Depending on the treatment site, temporary hair loss may occur, typically in the irradiated area.
Long-Term Effects: In some cases, radiation therapy can lead to long-term effects such as fibrosis (thickening of tissues) or damage to nearby organs. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare team can help monitor and manage these potential complications.
Coping Strategies and Supportive Care
To mitigate and manage side effects effectively, patients are encouraged to adopt the following strategies:
Skincare Regimen: Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products recommended by your healthcare team to nourish and protect the irradiated skin.
Hydration and Nutrition: Stay well-hydrated and maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support overall health and aid in recovery.
Physical Activity: Engage in light to moderate physical activities as tolerated, which can boost energy levels and improve well-being.
Open Communication: Maintain open and honest communication with your healthcare team regarding any side effects or concerns. They can provide guidance, medications, or adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Emotional Support: Seek support from family, friends, support groups, or counseling services to address emotional challenges and enhance coping mechanisms during treatment.
Summary
Radiation therapy remains a cornerstone of cancer treatment, offering targeted and effective tumor control while preserving the quality of life for many patients. With advancements in technology and the guidance of experienced radiologists like Dr. Snehal Suryawanshi, individuals undergoing radiation therapy can navigate their treatment journey with confidence, understand treatment options, manage potential side effects proactively, and embrace supportive care measures for optimal outcomes and improve the quality of life.